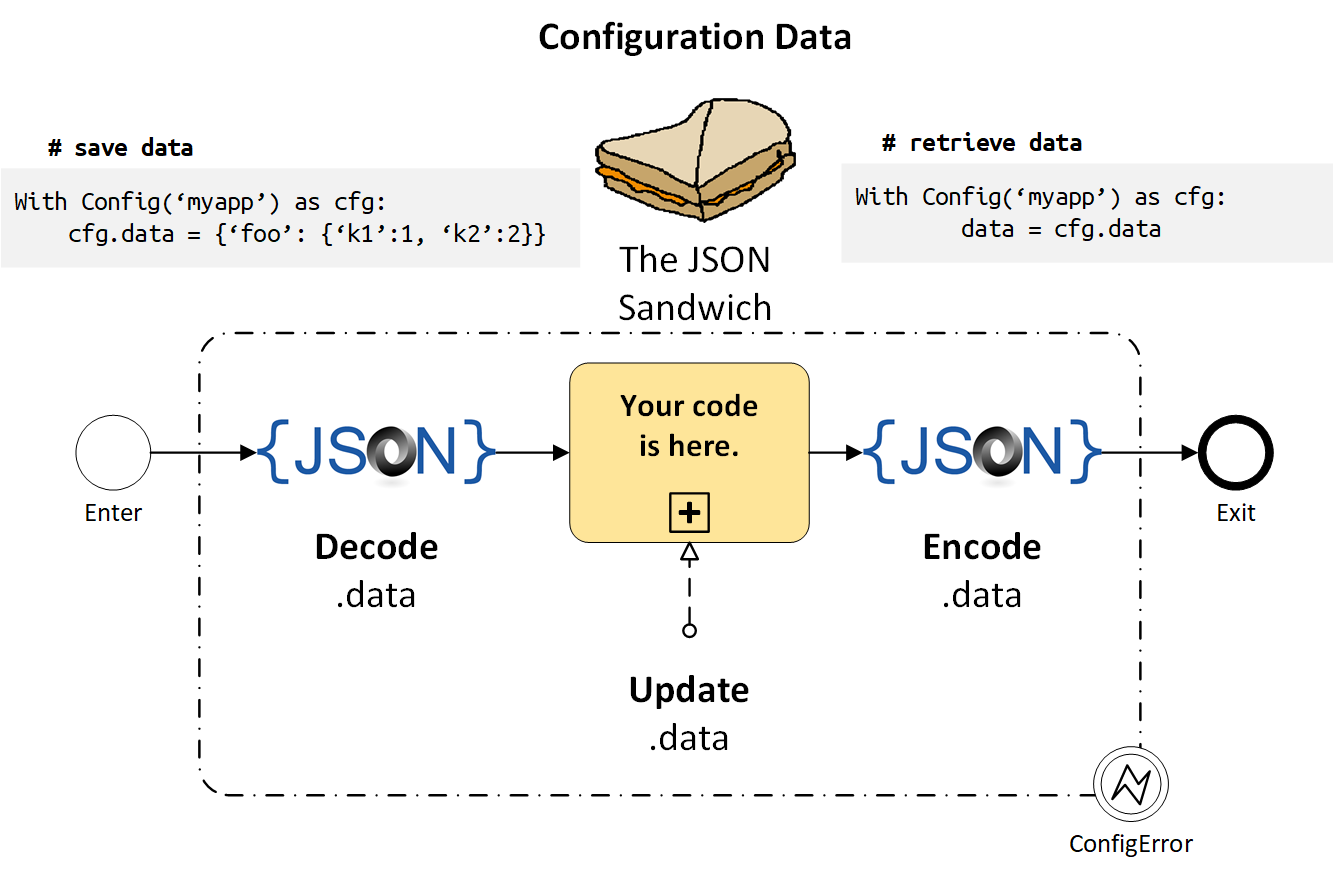
The JSON Sandwich¶
from jsonconfig import Config
with Config('myapp') as cfg:
cfg.data = {'debug': True}
Configuration data is stored in the context manager’s `data` attribute.
cfgfile is the filename; see the Configuration File Locations section to learn how it’s constructed:
Your data is in the middle of the sandwich …
- ENTER:
.data = json.load(cfgfile) - your code is here
- EXIT:
json.dump(cfgfile, .data)
That’s really all there is to it.
The Config context manager’s mode parameter determines whether the sandwich bread on the top, bottom, neither or both top & bottom.
- None
No access. Skip step 1 & 3. Do not read or write the data and do not expose the data attributed. This is useful is you are only interested in encrypted data and/or environment variables.
with Config('myapp', None) as cfg: pass
- r
Read-only mode. Skip step 1, set data = {}. Of course you can overwrite the data with any JSON serializable object, or apply one of Boxes data access wrappers, but by default it is a standard Python dict.
with Config('myapp', 'r') as cfg: configuration_data = cfg.data
- w
Write-only mode. Skip step 3. You update the data and it will serialize it as JSON and save it to the config file.
with Config('myapp', 'w') as cfg: cfg.data = {'debug': True}
- +
Read & write mode. This is the default. JsonConfig reads in your data and takes a snapshot (deepcopy) of it. You then update the data and then when it exits in step 3 (the context manager’s __exit__ method) it will compare the current data contents to the snapshot; if the data changed it will serialize the contents of the data attribute and save it to the configuration file.
with Config('myapp') as cfg: cfg.data.update({'width': 80})
Note
The above rules and automatic JSON encoding and decoding only apply to the data attribute.
The pwd (encrypted data) and env (environment variables) are updated as soon as you set them and retrieved on demand; they are strings by default. If needed, they can optionally be serialized as JSON using the to_json and from_json helper functions.